Reviewed for 2024
What's In This Post
Click to jump to section
What is a Compression Sock?
Compression socks are known by several names, depending on their intended use, design, or specific features. Some of these names include:
- Compression stockings: This term is often used interchangeably with compression socks and refers to the same type of garment that applies pressure to the legs and feet.
- Support stockings: This name emphasizes the supportive nature of compression socks, which help to alleviate discomfort, swelling, or fatigue in the legs and feet.
- Graduated compression stockings: This term specifies that the compression applied by the socks is graduated, meaning it is strongest at the ankle and gradually decreases towards the top of the sock.
- Medical compression stockings: This name is used when the compression socks are specifically designed for medical purposes, such as managing venous disorders or preventing deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Athletic compression socks: This term refers to compression socks that are designed for athletes or individuals participating in sports or physical activities. They are meant to enhance performance, reduce muscle fatigue, and promote faster recovery.
- Travel compression socks: These are designed for individuals who travel long distances or sit for extended periods, such as during flights, to help prevent swelling and reduce the risk of developing DVT.
- Anti-embolism stockings (TED hose): These are specifically designed for bedridden or post-surgical patients to help prevent blood clots and improve circulation.
Compression (mmHg)
Compression socks come in different levels of compression (pressure), measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) typically ranging from 15 - 20 mmHg up to 40 - 50 mmHg. You may also hear the term 'medical grade' when referring to compression levels.
When a manufacturer or healthcare provider says 'medical grade compression' they are typically referring to 'how' the garment is designed and manufactured: according to strict standards and guidelines to ensure their effectiveness and safety. Socks with higher pressure levels (such as 20 - 30 mmHg, 30 - 40 mmHg) are also more frequently called 'medical grade', although the lower compression level garments may also be manufactured according to medical grade standards.
To determine what mmHg compression level is right for you, consider consulting a medical professional who can assess your specific needs and advise you on the appropriate level of compression, sock length, and usage regimen. Doctors often prescribe medical compression socks as a non-invasive, cost-effective intervention to manage and alleviate the symptoms of various circulatory issues. If you have a prescription it also makes it easier for our team to help you narrow down your options, and pick the best compression sock for you to match your needs and style.
How Compression Socks Work
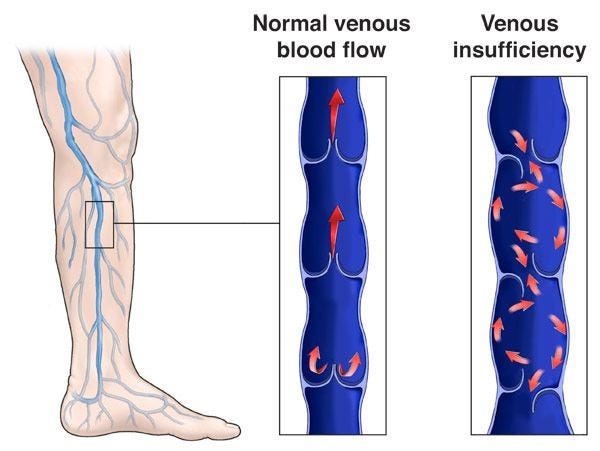
Compression socks work by applying gentle, consistent pressure to the legs and feet, which helps improve blood flow, reduce swelling, and provide support to the muscles and veins. They are typically designed with graduated compression, meaning the pressure applied is strongest at the ankle and gradually decreases as it moves up the leg. This design aids in promoting better blood circulation and preventing blood from pooling in the lower extremities.
The primary mechanisms through which compression socks work are:
- Enhancing blood flow: Graduated compression encourages blood to flow upwards, counteracting the effects of gravity and helping blood return to the heart more efficiently. This improved blood circulation ensures that the leg muscles receive adequate oxygen and nutrients.
- Supporting vein function: Compression socks provide external support to the veins, helping them maintain their shape and function, which is particularly important if the veins' walls or valves are weak or damaged.
- Reducing swelling: By promoting better blood circulation and preventing blood from pooling, compression socks can help minimize the swelling (edema) often associated with various medical conditions or prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Alleviating symptoms: Compression socks can help alleviate symptoms of various conditions, such as pain, aching, heaviness, and fatigue in the legs.
- Preventing complications: Consistent use of compression socks can help prevent or manage complications of certain conditions, such as varicose veins, skin changes, or venous ulcers.
Graduated vs. Uniform Compression
Graduated compression: Graduated compression socks apply pressure that is strongest at the ankle and gradually decreases as it moves up the leg. This design helps promote blood flow back towards the heart and is particularly effective for managing conditions related to blood circulation and venous disorders. Graduated compression is commonly used for:
- Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI)
- Varicose veins
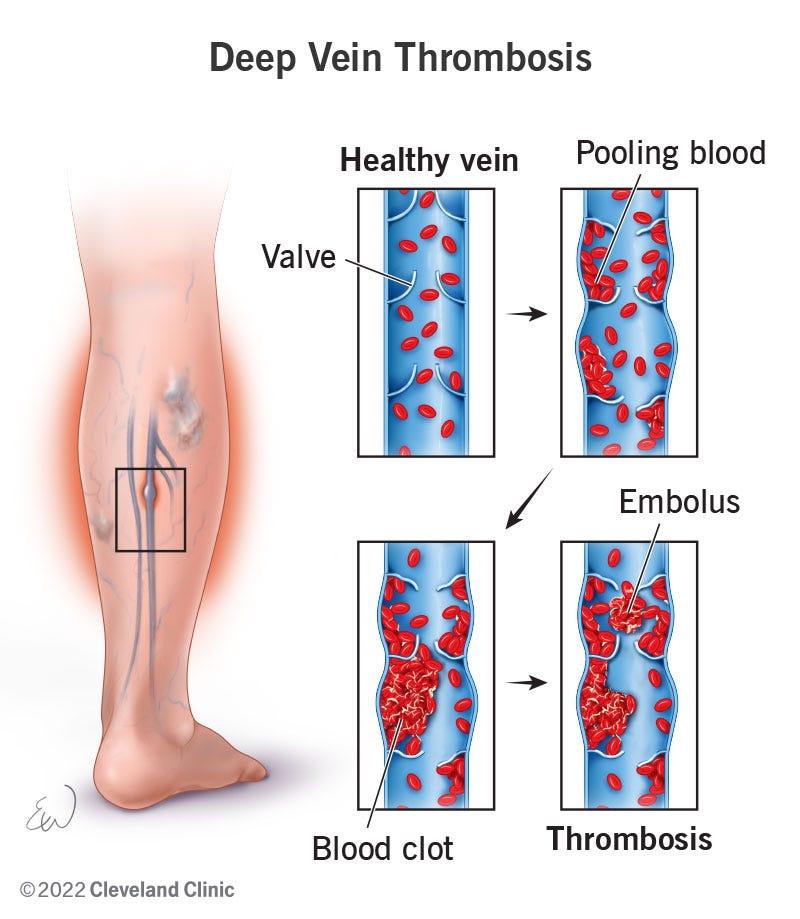
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prevention
- Lymphedema
- Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS)
- Pregnancy-related leg issues
- Athletic performance and recovery
- Prolonged standing or sitting
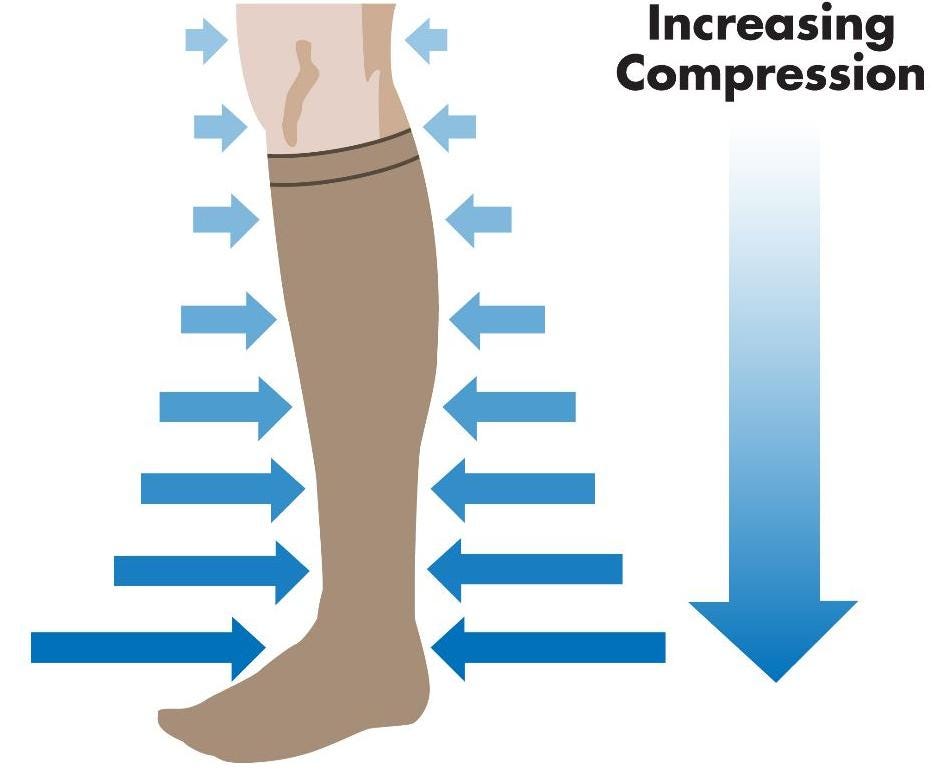

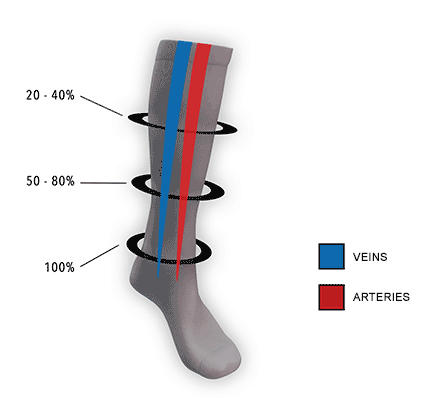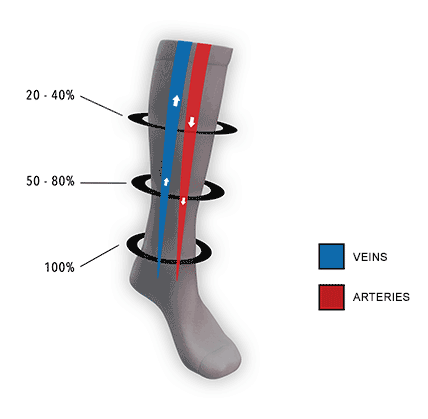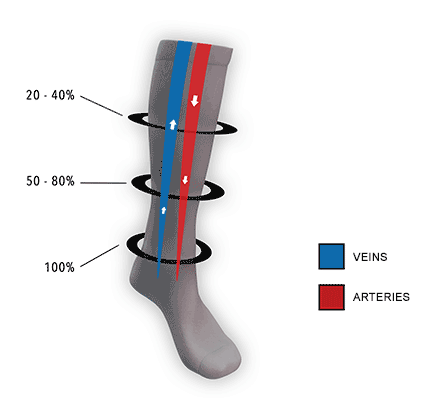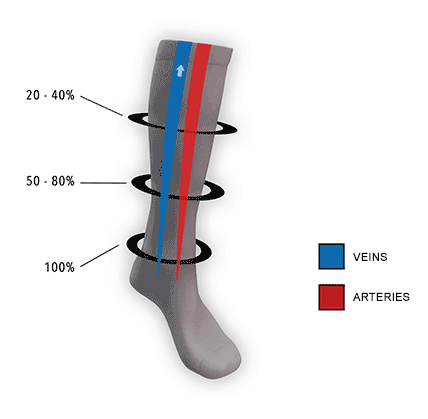

Consistent (uniform) compression: Consistent compression socks apply the same level of pressure throughout the garment, without any variation along the length of the sock. This type of compression is less common and is typically used for specific situations or conditions that require consistent support or pressure. Consistent compression may be used for:
- Certain types of edema that require uniform pressure
- Cases of lymphedema, particularly when wrapping or bandaging is not an option
You can read more about compression therapy for Lymphedema here.
Compression Socks and Stockings: For Medical Conditions
Compression socks can be used to treat, manage, or prevent a variety of medical conditions related to the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Some common medical conditions that can be addressed with compression socks include:
- Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI): Compression socks can help alleviate the symptoms of CVI, such as leg pain, swelling, and heaviness, by improving blood flow and supporting vein function.
- Varicose veins: Compression socks can help prevent the progression of varicose veins and alleviate symptoms like pain, swelling, and discomfort by promoting better blood circulation and supporting the veins.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Compression socks can be used to prevent DVT in high-risk situations, such as long-distance travel or post-surgery, by promoting blood flow and reducing the risk of blood clot formation.
- Lymphedema: Compression socks can help manage lymphedema by promoting lymphatic fluid drainage and reducing swelling in the affected limbs.
- Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS): Compression socks can help manage the symptoms of PTS, such as chronic pain, swelling, and skin changes, by improving blood flow and providing support to the veins.
- Diabetes-related foot issues: Diabetic patients can benefit from compression socks, as they promote better blood circulation, minimize swelling, and reduce the risk of foot injuries or complications.
- Post-surgical care: Patients recovering from surgery, particularly in the lower extremities, may use compression socks to prevent blood clots, reduce swelling, and promote healing.
- Pregnancy-related leg issues: Pregnant women can benefit from compression socks to alleviate leg swelling, discomfort, and reduce the risk of developing varicose veins or DVT


Important Note: Before you wear compression stockings to treat a medical condition, we recommend contacting your physician to ensure you are screened for conditions that increase the risk of complications prior to use. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before using compression socks to treat or manage any medical condition, as they can help determine the appropriate compression level, style, and proper fit for your specific needs.
Examples of Medical Compression Socks
-
 Mediven Select 20-30 mmHg Knee High StockingsAs low as $120.00
Mediven Select 20-30 mmHg Knee High StockingsAs low as $120.00
Use in Athletics, Tired Legs, Travel
Athletics: For athletes or individuals participating in sports or physical activities, compression socks can provide the following benefits:
- Improved blood circulation: The graduated compression promotes blood flow, which helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to the muscles more efficiently.
- Reduced muscle fatigue: Compression socks can help stabilize muscles, reducing vibrations and micro-tears that contribute to muscle soreness and fatigue.
- Enhanced recovery: By improving blood circulation, compression socks can help remove metabolic waste products from muscles, promoting faster recovery after exercise.
- Reduced risk of injury: Compression socks can help prevent muscle strains, shin splints, plantar fasciitis, and other injuries by providing additional support to the leg muscles and tendons. Special versions are available to treat Plantar
Tired legs: People who spend long hours on their feet or experience tired, aching legs can benefit from compression socks by:
- Reducing swelling: Compression socks can help minimize fluid buildup in the legs, reducing swelling and discomfort.
- Alleviating pain: By improving blood flow and providing support to the muscles, compression socks can help relieve pain and aching in the legs.
- Preventing varicose veins: Consistent use of compression socks can help prevent or alleviate the symptoms of varicose veins by promoting better blood circulation and vein function.
Travel: Compression socks can be particularly beneficial during long-distance travel or when sitting for extended periods, such as on flights or car rides. They can help:
- Prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Sitting for extended periods can increase the risk of blood clots in the legs. Compression socks promote blood flow and reduce the risk of developing DVT.
- Reduce leg swelling: Compression socks help prevent fluid buildup in the legs, which is common during long flights or car rides.
- Improve comfort: By reducing swelling and discomfort, compression socks can make long journeys more comfortable.
If you want to browse our Athletic Compression (including for travel and tired legs) you can view them Here.
Examples of Compression Socks for Athletics, Tired Legs, Travel
Compression Socks and Stockings: How to Choose a Style and Compression Level
Compression stockings are available in different designs, colours and compression strengths. You can get models in your size or individually made to measure, depending on your needs.
#1 Pick a Style - Below Knee, Thigh High, Full Waist, Waist with Attachment:
Compression socks and stockings come in different lengths to cover different parts of your body, from just below the knee, thigh-high and full waist high tights. What style you need depends on where the affected area is on your body. If you have swelling only in your ankles, then a knee-high sock would be appropriate. If you have swelling on or above the knee, then a thigh high or waist high compression stocking would be required.
There are a variety of stocking heights available, here some examples:
Fitting Tip:
Measurements should be taken in the morning before swelling occurs to get a true representation of size. Also, stockings applied in the morning will prevent swelling and must fit properly before swelling develops. Stockings should feel snug, but not painfully tight.
#2 Pick a Compression Level Based On What You Need The Garment For - Mild, Moderate, High:
Compression stockings have different levels of pressure, measured in mmHg. Mild compression is designed to keep you comfortable on your feet at work or improve performance during sports. You'll need higher compression with a firmer fit for venous disease or to prevent DVT (a type of blood clot called deep vein thrombosis). As you move into the higher compression levels (20 - 30, 30 - 40) it is a good idea to speak with your doctor first to get a prescription for medical compression. Your doctor will make sure compression therapy is safe for you, and advise you on the appropriate level of compression, sock length, and wearing duration. In most cases having a prescription will also remove any sales taxes from your purchase.
Mild Compression (15 - 20 mmHg) - Use For Traveling, Work, Sports, Daily
When traveling, at work, or during sports and activity - light compression support and stockings can promote better blood flow and reduce swelling. This may help with improving physical performance, reducing soreness, and fatigue. Typical diagnosis for this compression type are for individuals with no visible signs of venous disorders, or spider veins.
Mild compression stockings are comfortable to wear and beneficial for your legs - regardless of the situation you can always find the best stocking to suit your needs. For mild compression, there is a higher elasticity component for added comfort so over the course of the day the garment has more “give” to the shape. Here are some examples of mild compression rated socks:
Bauerfeind Compression Sock Training:
Decrease muscle 'vibration' to reduce fatigue in the muscle. Mimics taping technique for extra ankle support and a protective zone for more comfort around the Achilles tendon.
Bauerfeind Compression Sock Performance:
Most recommended for endurance sports because it promotes good calf muscle refill. It has a higher elasticity context and a wide top band for more comfort. Additional features include more space at toes and moisture wicking fabric.
Bauerfeind VenoTrain Discretion:
The exceptionally fine material of these compression stockings gives them a stylish transparency and lightness.
Mild to Moderate Compression (20 - 30 mmHg) - Use For spider veins, varicose veins, swollen ankles
To minimize the risk of spider veins, varicose veins and swollen ankles moderate compression promotes blood circulation so that your legs still feel light even at the end of a long day. The mild to moderate compression options have a decrease in their elasticity component and an increase in working pressure. This means the garment has an increased ability to keep the same compression level over the course of the day. This is typically used for spider veins, varicose veins and imminent functional insufficiency.
Here are some examples of moderate compression rated socks:
Bauerfeind Compression Sock Merino
Featuring a high content of Merino Wool for every-day wear
Higher elasticity. Comes with pressure relief zones on foot and heel. Wider toes for less friction and available in an open toe design.
Bauerfeind VenoTrain Business:
Trouser sock offers a wide toe seam. Thicker material than the other available options. Holds shape as it has a higher working pressure compared to the VenoTrain Look and VenoTrain Micro.
High working pressure so it holds its shape well. Not as soft as the VenoTrain Micro.
More room at heel and less material at the front of the ankle for added comfort for individuals with restricted mobility (wheelchair).
Moderate to High Compression (30 - 40 mmHg) - Use for more severe varicose veins, edema, functional insufficiency
Compression garments are an important part of therapy for venous disease. Venous disorders are chronic, incurable diseases. But with strong compression you can alleviate your symptoms and help slow down the progression of the disease: whether spider veins, varicose veins, varicose veins with edema or functional insufficiency - moderate to high compression options have a low elasticity component and an increase in working pressure. This means the garment keeps the same compression level over the course of the day and is typically used for individuals with varicose veins, varicose veins with edema and functional insufficiency. For these higher mmHg levels, the appropriate (safe) level of compression is determined by a healthcare professional based on the specific medical condition, its severity, and the patient's individual needs.
Here are examples of moderate to high compression rated socks:
More Tips:
- Hand washing socks in warm water and air drying will return the garment to original shape.
- Shelf life of these products is 6 months if worn every day. Compression level will not be the same after one year so a new pair should be ordered every year.
- Reminder: Don't forget to consult your doctor or healthcare practitioner to determine if compression therapy is right for you.
- Looking for tips on how to measure for compression socks and stockings? check out our other article How To Measure For Compression Socks & Stockings To Get The Right Fit
Browse our full line of medical compression stockings, here like these: